 We are so pleased to have Lindsey Wells, ND, join in our series of Q&As on COVID-19. Her focus will be on zinc and more!
We are so pleased to have Lindsey Wells, ND, join in our series of Q&As on COVID-19. Her focus will be on zinc and more!
Dr. Lindsey Wells is a naturopathic physician. Dr. Wells has focused her practice on consultative care for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), PANS/PANDAS, Lyme and Co-Infections, other neurodevelopmental disorders, and various chronic illnesses. She uses therapies, including homeopathy, botanical medicine, nutraceuticals, nutrition, counseling, and water therapy. This model of care addresses the biochemical, nutritional, and energetic needs of each patient to improve overall health. For her complete bio and more information, please see her website.
Please Note: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a new strain that was discovered in 2019 and has not been previously identified in humans. The WHO is closely monitoring and updating the information regularly. Recommendations regarding prevention and treatment will change and evolve as more data is processed. It is essential to communicate with your Primary Care Provider (PCP) directly regarding you and your family’s unique healthcare needs. WHO
Gabriella: Thank you for joining us again to talk about COVID-19. Today Dr. Wells is going to focus on zinc, resveratrol, and Chinese Skullcap. But first, let’s do a review of COVID-19 symptoms.
Lindsey:
Most Common Symptoms
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of Breath
Other Symptoms
- Aches and Pains
- Sore Throat
- Fatigue
- GI Symptoms
- Losing Sense of Smell OR overpowered with a sense of smell
Emergency Warning Signs to seek immediate medical attention:
- Trouble Breathing
- Persistent Pain or Pressure in the Chest
- New Confusion or Inability to Arouse
- Bluish Lips or Face
Source: CDC
COVID 19 and Skin Rashes
Gabriella: I saw a few articles about rashes being associated with COVID29, can you speak to that?
Lindsey: Yes, absolutely.
COVID 19 and Skin Rashes
Present as similar rashes to other viral illnesses:
- Erythematous exanthem
- Acute urticaria
- Chicken-pox like blisters
- Transient livedoid eruptions
Source: Manalo IF, Smith MK, Cheeley J, Jacobs R, A Dermatologic Manifestation of COVID-19: Transient Livedo Reticularis, Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (2020), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.018.
Skin manifestations were observed in about one-fifth of a group of patients with COVID-19 in the Alessandro Manzoni Hospital in Lecco, in northern Italy.
Dermatologists were recruited to look at what was going on with the skin in COVID-19 inpatients. Of the 88 COVID-19 patients, ~21% developed skin manifestations. 44% of those patients had skin eruptions at symptom onset, and the rest after hospitalization. The skin manifestations presented as red rashes, widespread urticaria, and chickenpox-like vesicles. The most commonly affected area was the trunk. Itching was mild or absent, and lesions usually healed up in a few days. Most importantly, skin manifestations did not correlate with disease severity.
They described a case of a COVID-19 infection in a Bangkok hospital that resembled dengue fever. The person presented with only a skin rash, petechiae, and a low platelet count consistent with Dengue Fever. The authors concluded that COVID-19 can present with a rash and be mistaken for dengue. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar 22. pii: S0190-9622[20]30454-0. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.036).
Source: Cutaneous manifestations in COVID‐19: a first perspective, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16387
COVID-19 and Zinc
Gabriella: Zinc. One of my heroes. If I don’t get adequate zinc, I swear I get sick as soon as I go outside. Maybe a bit of an exaggeration but I never miss taking it.
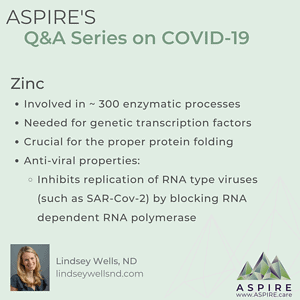 Lindsey: Yes, supplementing zinc is important for many people
Lindsey: Yes, supplementing zinc is important for many people
- Involved in ~ 300 enzymatic processes
- Needed for genetic transcription factors
- Crucial for the proper protein folding
- Anti-viral properties:
- Inhibits replication of RNA type viruses (such as SAR-Cov-2) by blocking RNA dependent RNA polymerase
Zinc Study 1:
Title: Effect of zinc salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Discussion: Zinc supplementation decreases the morbidity of lower respiratory tract infection in pediatric patients in the developing world. This study looked at the inhibitory effects of 3 zinc salts (acetate, lactate, sulfate) on the replication of RSV.
- They found >1000 fold reduction in RSV yield when zinc was present
- Therefore the results suggest that zinc mediates antiviral activity on RSV by altering the ability of the cell to support RSV replication
Source: Suara RO, Crowe JE Jr. Effect of zinc salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2004 Mar;48(3):783-790. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.3.783-790.2004.
Zinc Study 2:
Title: The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity
Discussion: “Zinc is an essential trace element that is crucial for growth, development, and the maintenance of immune function. Its influence reaches all organs and cell types, representing an integral component of approximately 10% of the human proteome, and encompassing hundreds of key enzymes and transcription factors”.
- Review of zinc’s antiviral properties: “An abundance of evidence has accumulated over the past 50 y to demonstrate the antiviral activity of zinc against a variety of viruses, and via numerous mechanisms”.
- Zinc deficiency common in ¼ of the population of developing countries. Seen in populations most at risk for certain infection such as HIV, Hep C
- This review goes through the mechanisms of action making zinc a potent antiviral
Source: Read SA, Obeid S, Ahlenstiel C, Ahlenstiel G. The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity. Advances in Nutrition (Bethesda, Md.). 2019 Jul;10(4):696-710. DOI: 10.1093/advances/nmz013.
Zinc Study 3:
Title: Zinc supplementation for the prevention of pneumonia in children aged 2 months to 59 months.
Discussion:
- In 2015 pneumonia was the largest cause of childhood mortality under the age of 5 years old.
- WHO reported zinc deficiency accounted for 13% of all lower respiratory tract infections
Source: Lassi ZS, Haider BA, Bhutta ZA. Zinc supplementation for the prevention of pneumonia in children aged 2 months to 59 months. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 Dec(12):CD005978. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.cd005978.pub2.
COVID-19, Zinc & Ionophores
Zinc and Ionophores
In general, the intracellular concentration of free zinc is low. Zinc in solution exists in ionic form (Zn2+). In this form, it contains 2 extra electrons it doesn’t need. Cells don’t like zinc in this form because at high levels it can cause apoptosis (cell death) and interfere with protein synthesis.
In order to get higher levels into the cell, there needs to be assistance by zinc ionophores. Ionophores reversibility bind the ions so they can facilitate the entry of zinc into the cell. By getting zinc into the cell at higher concentrations, it can exhibit its antiviral properties by inhibiting the replication of RNA viruses; COVID 19 is an RNA virus.
 Ionophores
Ionophores
- Quercetin
- EgCg
- Reservatrol
- Chloroquine
- Ivermectin
Source: Juarez M, Schcolnik-Cabrera A, Dueñas-Gonzalez A. The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8(2):317–331. Published 2018 Feb 1.)
Zinc and Ionophores Study 1:
Title: Zinc Ionophore Activity of Quercetin and Epigallocatechin-gallate: From Hepa 1-6 Cells to a Liposome Model
Discussion:
- Quercetin is a great antihistamine, anti-inflammatory, and is immunomodulatory
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is a potent antioxidant
- Both of these are polyphenols and flavonoids
- This study showed that these polyphenols are zinc ionophores by transporting zinc cations (a positively charged ion) across the plasma membrane
- This study showed a rapid increase in zinc in mouse hepatocarcinoma help 1-6 cells and in liposomes
Source: Zinc Ionophore Activity of Quercetin and Epigallocatechin-gallate: From Hepa 1-6 Cells to a Liposome Model J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 32, 8085-8093, July 22, 2014 DOI: 10.1021/jf5014633
Zinc and Ionophores Study 2:
Title: Chloroquine Is a Zinc Ionophore
Discussion:
- Chloroquine is an anti-malaria drug
- Chloroquine has antiviral properties based on two mechanisms
- Endosome alkalinizer
- Enveloped viruses (like COVID 19) make a bubble-like structure around themselves called an endosome
- In order to initiate replication, the endosome must have a low Ph (acidic).
- Chloroquine can be taken up by the endosome and since chloroquine has an alkaline pH it will increase the PH in the endosome, so the virus cant replicate
- Zinc Ionophore
- This study investigated further, chloroquines’ anticancer properties by looking into the interaction of zinc ions with chloroquine in ovarian cancer cell lines
- Found that chloroquine enhanced zinc uptake by ovarian cancer cell lines
- Concluded that chloroquine with zinc enhances chloroquine’s cytotoxicity and increased apoptosis (cell death) in the cell line
- Endosome alkalinizer
Source: Xue, Jing & Moyer, Amanda & Peng, Bing & Wu, Jinchang & Hannafon, Bethany & Ding, Wei-Qun. (2014). Chloroquine Is a Zinc Ionophore. PloS one. 9. e109180. 10.1371/journal.pone.0109180.
Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine
The majority of COVID-19 testing is on chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine used for a long time to prevent and treat malaria; it is also a therapy against rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. The hope is that the cases will be mild or help protect against coronavirus if given before infection or during the early course of the disease.
Source: Chloroquine, Zinc Tested to Block COVID Infection, Karen Weintraub, WebMD, April 9, 2020
Zinc and Ionophores Study 3:
Title: Effect of resveratrol and zinc on intracellular zinc status in normal human prostate epithelial cells
Discussion:
- Evaluated the influence of resveratrol on zinc in human prostate epithelial cells.
- There was a reduction in cell growth in cells treated with resveratrol
- Dramatic increase in cellular total zinc concentration in those subjects being supplemented with zinc
Source: Effect of resveratrol and zinc on intracellular zinc status in normal human prostate epithelial cells. Jun Jun Zhang, Min Wu, Norberta W. Schoene, Wen-Hsing Cheng, Thomas T. Y. Wang American Physiological Society, 01 Sep 2009 https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00139.2009
Resveratrol
- Natural polyphenol found in many plant species, grape skins and seeds, and wine
- Anti-oxidant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antimicrobial – Phytoalexin that acts against bacteria, viruses and fungi
- Neuroprotective
- Cardiovascular protectant
- Anti-carcinogenic by inhibiting initiation, promotion and progression
- Resveratrol is a stilbenoid polyphenol, possessing two phenol rings linked to each other by an ethylene bridge.
- Trans-form is dominant in terms of its prevalence and different biological activities are attributed, namely in inducing cellular responses such as cell cycle arrest, differentiation, apoptosis, and to enhance cancer cells anti-proliferation
- Wells’s preferred source of Trans-Resveratrol is Japanese Knotweed.
- Also found in blueberries, raspberries, dark chocolate, pistachios, peanuts
Reservatrol Study 1:
Title: Effective inhibition of MERS-CoV infection by resveratrol
Discussion:
- Resveratrol inhibited MERS COV infection
- Prolonged cellular survival after virus infection by downregulating apoptosis induced by MERS
- Reservatrol decreased expression of nucleocapsid protein essential for MER COV replication
- Conclusion: resveratrol potent anti-MERS agent
Source: Lin, S., Ho, C., Chuo, W. et al. Effective inhibition of MERS-CoV infection by resveratrol. BMC Infect Dis 17, 144 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2253-8
Chinese Skullcap/Baicalin
- Aka Scutellaria baicalensis
- Potent anti-inflammatory
- Anti-microbial
- Antioxidant
- High in polyphenols contributing to anti-cancer properties
Source: Wang et al., Polyphenols of Chinese skullcap roots: from chemical profiles to anticancer effects, RSC Adv., 2019
Sowndhararajan, Kandhasamy et al. “Neuroprotective and Cognitive Enhancement Potentials of Baicalin: A Review.” Brain sciences vol. 8,6 104. 11 Jun. 2018, doi:10.3390/brainsci8060104
Chinese Skullcap/Baicalin Study 1:
Title: Scutellaria baicalensis extract and baicalein inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2 and its 3C-like protease in vitro
Discussion:
- This study looked at Chinese skullcap anti-viral activity against COVID 19
- They investigated its impact on COVID 19 main protease called 3C-like protease (3CL pro) this is a highly conserved protease across coronaviruses and is essential for the maturation process of viral polyproteins
- They found that the ethanol extract of Chinese skullcap inhibited the COVID 19 3CL proactivity in vitro and the replication of COVID 19
- The major component of the plant responsible was baicalein
Source: Scutellaria baicalensis extract and baicalein inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2 and its 3C-like protease in vitro. Hongbo Liu, Fei Ye, Qi Sun, Hao Liang, Chunmei Li, Roujian Lu, Baoying Huang, Wenjie Tan, Luhua Lai, bioRxiv 2020.04.10.035824; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.10.035824
Gabriella: Thank you, Dr. Wells. This provided us with clarity on this matter. We appreciate that you took time out of your busy day to speak with ASPIRE!
Dr. Lindsey wells and her colleagues at New England Center for Health are continuing to host a series of zoom calls on COVID-19. The schedule will be updated weekly.
One comment to COVID-19 Zinc and More with Lindsey Wells, ND
Rob
August 23, 2020Is Ivermectin a zinc ionophore?.