
Nutrition for PANS & PANDAS
Nutrition is vital for kids with PANS/PANDAS, conditions tied to OCD and infections like strep that disrupt eating habits, causing nutrient deficiencies and gut issues. Registered Dietitians (RDs)...

Nutrition is vital for kids with PANS/PANDAS, conditions tied to OCD and infections like strep that disrupt eating habits, causing nutrient deficiencies and gut issues. Registered Dietitians (RDs)...
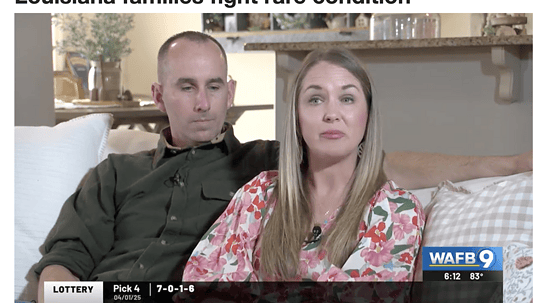
PANS or PANDAS refers to what some doctors call Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infections. It’s an often misunderstood and misdiagnosed disease that...
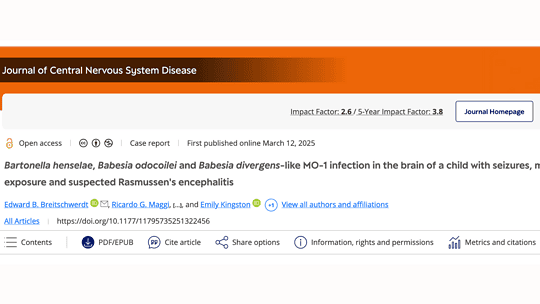
Imagine a child suffering from seizures, only to discover years later that the cause might be tied to a cat scratch and an insect bite. A groundbreaking case study from North Carolina State...
Students with PANS/PANDAS have complex cognitive, behavioral, physical & neurological symptoms that affect their school performance. The school's multidisciplinary team benefits from an awareness of...

Living with a sibling affected by PANS profoundly impacts well-being—fear of outbursts, limited social opportunities, and the isolation of not having the words or knowledge to explain the...
Supporting Students with PANS, PANDAS, and Basal Ganglia Encephalitis: Children with PANS, PANDAS, and basal ganglia encephalitis often require specific school accommodations to support their...
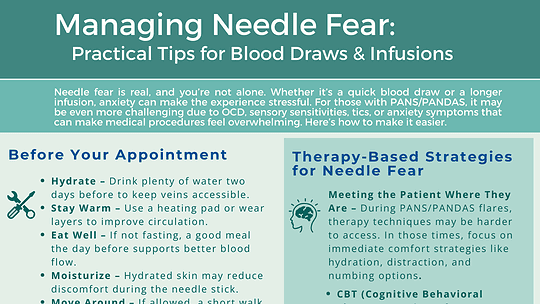
Needle fear is real, and you’re not alone. Whether it’s a quick blood draw or a longer infusion, anxiety can make the experience stressful. For those with PANS/PANDAS, it may...
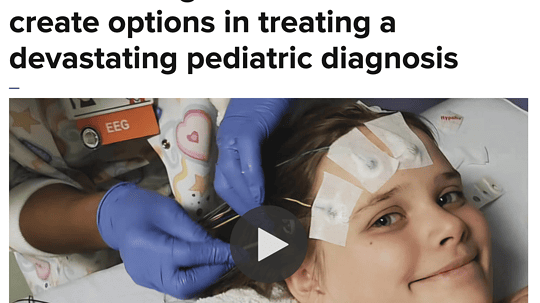
The bill is going to be a huge step forward, but Emily‘s mom April says it’s not a cure the bill does not mandate insurance coverage for the most common and effective...